Summary_Nervous system and sense
# Why do neurons differ from other cells?(3p)
Special membrane with ion channels → negative charge inside, positive outside
excitable because of that
# What is the charge of the resting potential and the action potential? Which happens when the neuron gets a stimulus? (3p)
resting potential: -70mV
action potential : +30mV
action potential is reached when the cell is stimulated
# Name the 3 types of neurons with their tasks! (6p)
- sensory neurons
- interneurons
- motor neurons
# Name the 2 parts of the nervous system with their parts! (6p)
central nervous system - brain , spinal cord
peripheral nervous system - ganglia, nerves
# Name the parts of the brain diagram! (cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem, diencephalon) (4p)
# Where can you find the medulla! Name 3 functions of the medulla! (4p)
in the brainstem
regulation of
- blood pressure
- breathing
reflexes
- sneezing
- coughing
- swallowing
- vomiting
# Where belongs the hypothalamus! Name 3 functions of the hypothalamus! (4p)
diencephalon
- thermal regulation
- daily physiological cycles
- endocrine system
- controlling appetite
# What are the tasks of the cerebellum? (4p)
- posture control
- movement coordination
- balancing and learned movements
- precise movement
# Compare the somatic and the autonomic nervous system! (5p)
| somatic | autonomic |
|---|---|
| voluntary movement | involuntary body functions |
| external environment | internal environment |
# Name the 2 ways of regulation in the autonomic nervous system! Compare them in 2 points! (6p)
| sympathetic | parasympathetic |
|---|---|
| fight or flight system - uses a lot of energy | reserves resources |
| increased heart and breathing rate, blood goes to muscles | slower heart rate, slower breathing, blood goes to digestive system |
# Fill the gaps of the chart about the sense organs! (6p)
| eyes | ears | nose | tongue | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| stimulus | photon | sound | smell | taste |
| receptors | photoreceptors | mechanoreceptor | chemoreceptor | chemoreceptor |
# What is the task of the lens and the pupil? (4p)
lens - focuses light by changing its shape
pupil - controls the amount of light entering the eye
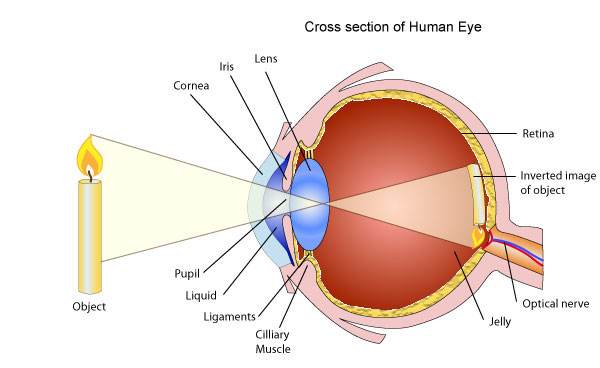
# Name the 2 receptor types of the retina with their task! (5p)
rods - sense light
cones - sense colors
# Where can be found the receptors of hearing? What can they sense?
cochlea
movement of the fluid
# Which part of the ear intensifies the vibration? What is the frequency range we can sense? (4p)
middle ear - 3 bones connecting the eardrum and cochlea
20-20 000 Hz
# What can we sense with our nose and tongue? (3p)
water soluble chemicals which dissolve in the mucus of the nose and saliva
# List the receptor types of the skin with 1 stimulus they can sense! (6p)
mechanoreceptors - touch, pressure, vibration
thermoreceptors - difference in cold and warm
pain receptors - (free nerve endings on the top of the dermis )